When taking part in Frank Lloyd Wrights preeminent architectural school known as the Taliesin Fellowship, Lois Gottlieb came to understand architecture as a kind of Lebensphilosophie, in that she came to consider it a mode of living that touched on and derived inspiration from all aspects of life. Hence the title of her account of her apprenticeship A Way of Life, which deftly highlights the interplay of the rarefied and the mundane, the interdependence of humans and their natural surroundings, and the fluidity between the concreteness of day-to-day living and abstract worldview. Furthermore, it presents art as an act of cultivation and sustained effort, rather than a quasi-mysterious realization of personal genius.
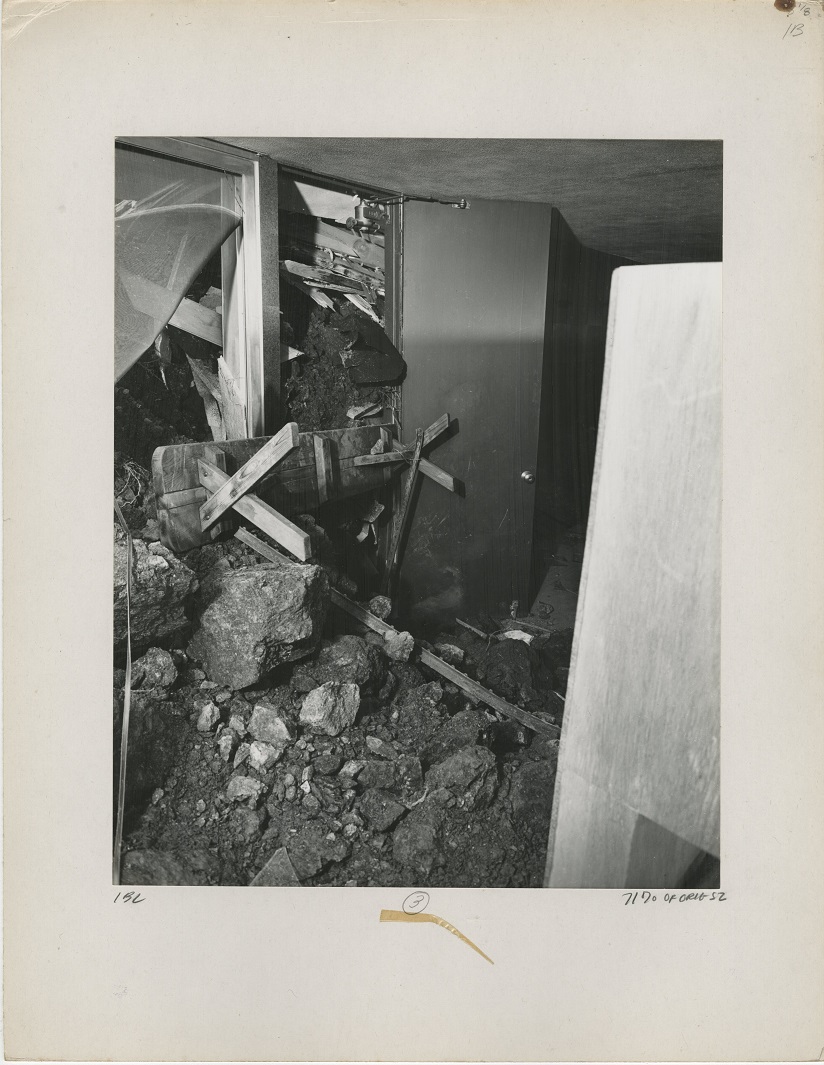
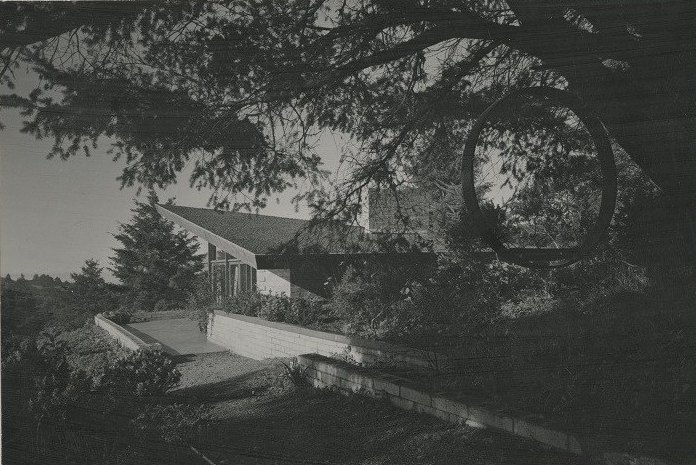
It’s of note that Wrights teaching style deviated significantly from the norms of his time and tended to subvert the traditional master-apprentice relationship. His radically egalitarian approach to pedagogy came to inform Gottliebs own teaching style and her outlook on the ways humans shape and control the environment. Her first major publication, the book Environment and Design in Housing, first workshopped as a series of lectures at UC – Riverside, articulates the effects of design on both the micro- and macro-scale, i.e., the way the [physical] environment we each create for ourselves and our families does affect every part of our lives [1] and the implications of poor design in terms of ecological sustainability and financial cost. In her view, humans have an unrivaled capacity to adapt the environment to their needs – a capacity that is problematic at scale and exacts high tolls, both from the land itself and from people affected by landslides or other natural disasters (see picture below). In light of these concerns, she advocates a more thoughtful approach based on client needs and leveraging the natural assets of building sites rather than the one-size-fits-all attitude of traditional design. (As a side note, Julius Shulman, famed architectural photographer, worked with Gottlieb on this book as photography consultant. The work itself features many of his gorgeous black-and-white photographs, prints of which are available for viewing as part of Gottliebs architectural collection here at Virginia Tech. Two copies of Environment and Design in Housing are also available for research as part of Special Collections selection of rare books – the captions and broader expositions provide invaluable context for the photographs.)

Design and Gender Norms
A notable feature of this book is its emphasis on practice and its demystification of architectural knowledge. While much of Gottlieb’s approach is informed by cultivating self-knowledge and considering the dwelling as a vehicle for personal expression, it tends to balance this view with injunctions to draw on the specialized knowledge of experts – lending itself to a kind of tempered humanism and recognition of personal limitations. This methodology, I think, can also be traced to Gottliebs time spent at Taliesin, which, for the time, was certainly unique in its combination of self-reliance and communal dependencies.
A different, but related, novelty of the schools social structure was its disregard for gender norms. It is generally recognized these days that, historically, there have been gender-inflected labor divisions in both the public and domestic sphere. At Taliesin, these traditional divisions were not enforced – men would often perform tasks like preparing dinner while women would thresh wheat. Homemaking was not the strictly circumscribed domain of women, nor was outdoor labor the exclusive domain of men. While her works primary focus isnt on cultural assumptions regarding women, Gottlieb clearly has thoughts on the connections between gender and under-recognized labor. On the subject of domesticity, design, and value, she offers the following observations:
Another attitude toward the occupation of homemaking is that it is nothing or of little importance. An answer to the typical question What does Jane Doe do? is Oh, nothing, or She doesnt work, she is just a housewife. Yet this housewife is supposed to do most of the buying for the family, keep them all in good physical condition, keep them attractively housed and clothed, see to it that the children are educated, and so on and on.
In other situations any of these tasks is considered a field of specialized knowledge…But the homemaker is supposed to have absorbed and be all these things at once, a sort of twentieth-century version of the Renaissance man (without any of the credit for doing so, presumably).[4]
It’s clear that Environment and Design in Housing is at least partially intended to serve as a practical resource for homemakers. It’s also clear that the book is meant to bring analysis to typically underserved segments of society and to address real (if hidden) needs.

References
1. Lois Davidson Gottlieb, Environment and Design in Housing (New York: Macmillan, 1966), 1.
2. Gottlieb, 5.
3. Lois Davidson Gottlieb Architectural Collection, Ms1997-003, Special Collections, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, Va.
4. Gottlieb, 231.










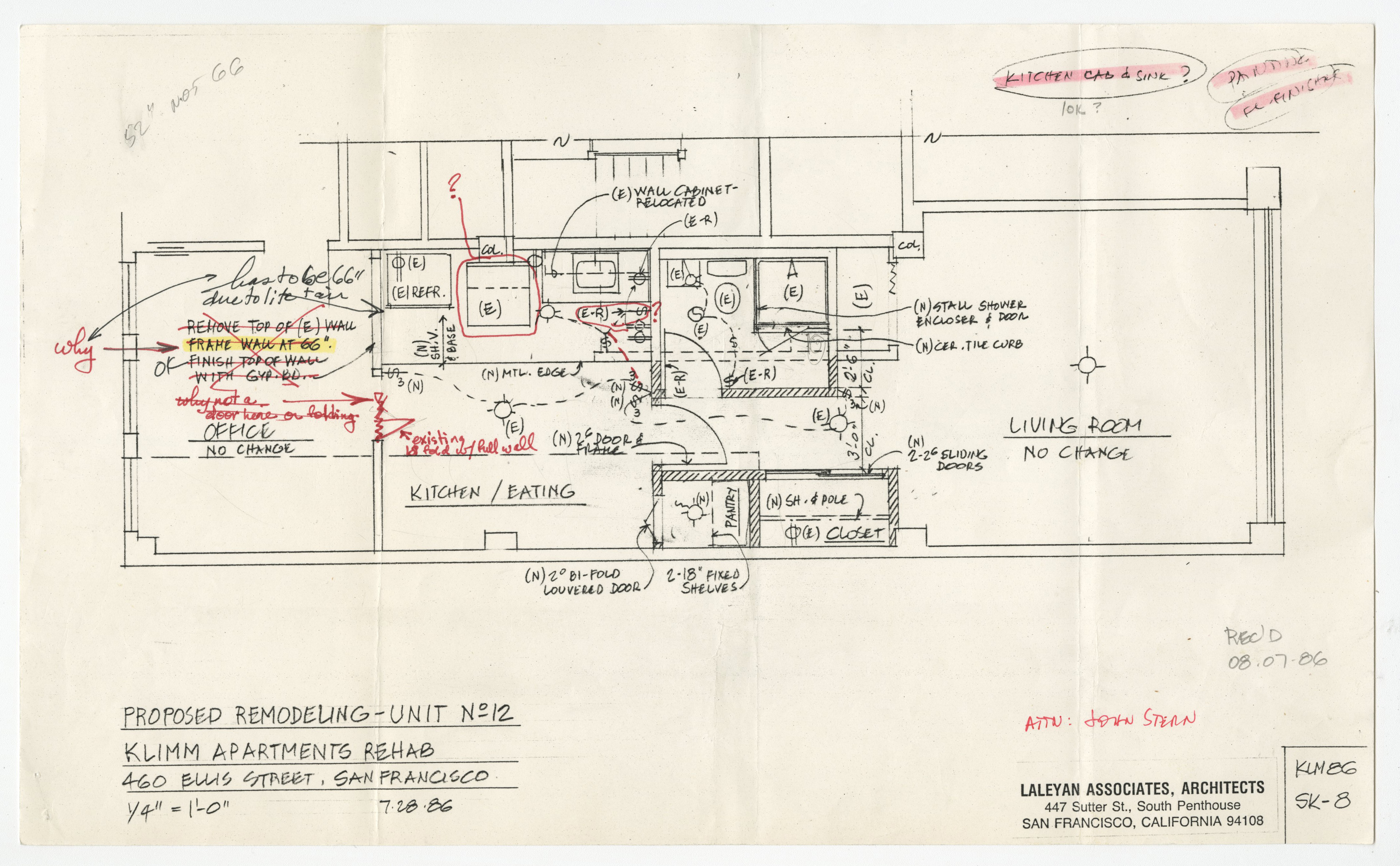
 In reference to a letter from a contractor, Laleyan notes in section A that I do not challenge contractors. I administer the construction contract as required by my agreement and later notes occasionally contractors have disagreed with my interpretation of the contract documents, but you are the first who has challenged persistently my authority to interpret those documents and my right to make decisions, based on those interpretations.
In reference to a letter from a contractor, Laleyan notes in section A that I do not challenge contractors. I administer the construction contract as required by my agreement and later notes occasionally contractors have disagreed with my interpretation of the contract documents, but you are the first who has challenged persistently my authority to interpret those documents and my right to make decisions, based on those interpretations. The notes in the last section recount Laleyan’s experience ofbeing yelled at in front of a job superintendent, workers, and others. She goes on to mention that while she did not respond on grounds of professional behavior, she will not tolerate a project development supervisor undermining her authority with the contractor.
The notes in the last section recount Laleyan’s experience ofbeing yelled at in front of a job superintendent, workers, and others. She goes on to mention that while she did not respond on grounds of professional behavior, she will not tolerate a project development supervisor undermining her authority with the contractor. Laleyan notes that she would appreciate it if her designs were followed and not improved upon by the contractor.
Laleyan notes that she would appreciate it if her designs were followed and not improved upon by the contractor.