To celebrate womens history month, we are highlighting a small selection of the pioneering women professionals in our collections. These particular women entered their respective careers in the 1950s and 60s, a time when women had limited access to higher education and professional opportunities. Women in historically marginalized groups (including LGBTQ communities, rural communities, and communities of color) faced additional challenges beyond gender barriers. The four women profiled below overcame several obstacles to work as accomplished professionals in fields traditionally dominated by men.

Marjorie Rhodes Townsend: Aerospace Engineer, Patent Holder
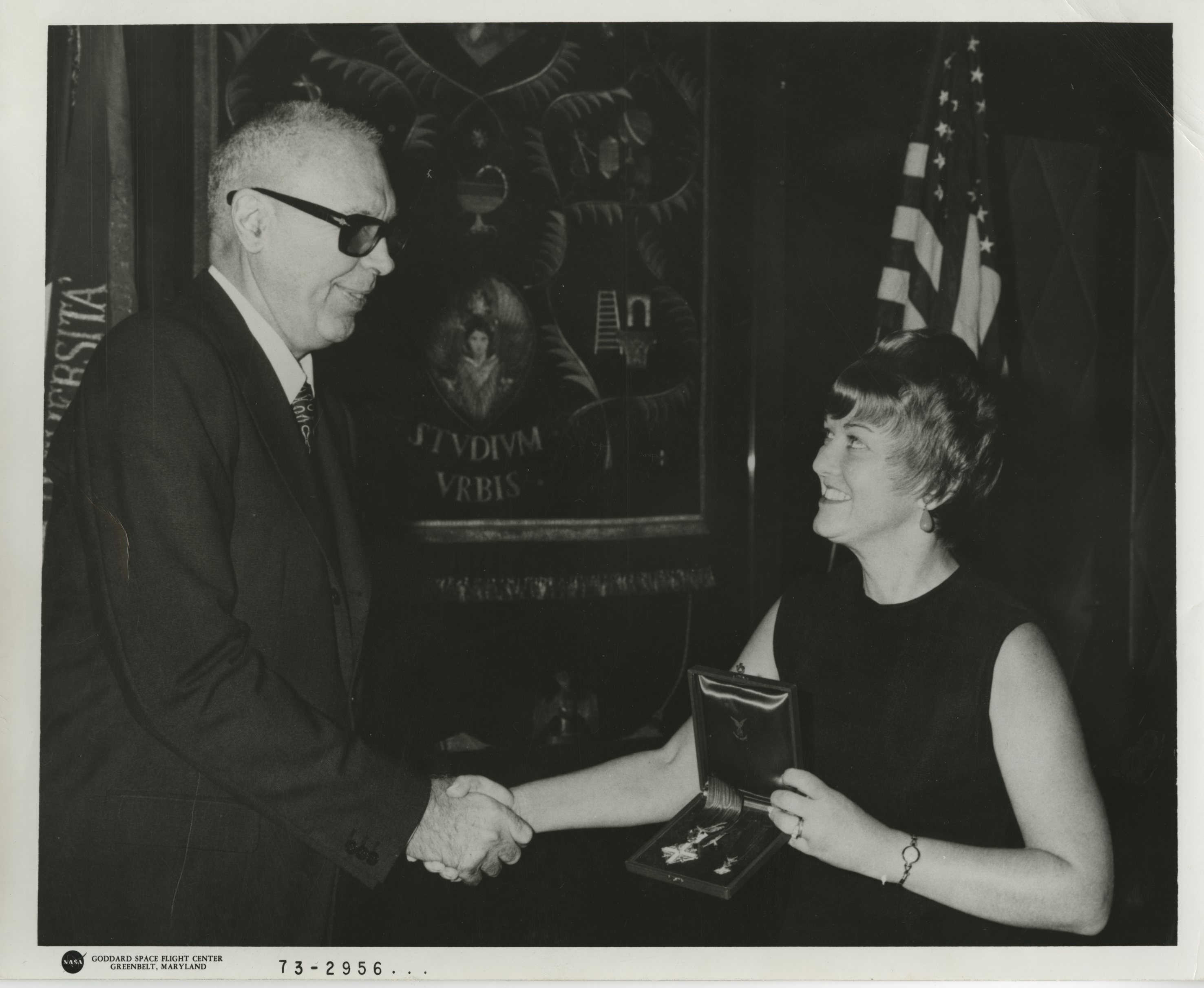

In 1951, Marjorie Rhodes Townsend became the first woman to earn an engineering degree at George Washington University. One of few women in a traditionally male-dominated field, Townsend experienced significant discrimination from both coworkers and managers. In spite of these challenges, she enjoyed a lengthy and distinguished career at the forefront of aerospace technology. Townsend spent eight years with the Naval Research Laboratory developing sonar signal-processing devices for anti-submarine warfare. Townsend went on to work for the National Aeronautics and Space Administrations Goddard Space Flight Center from 1959-1980. As a project manager for NASAs Small Astronomy Satellite (SAS) program, Townsend helped coordinate some of the earliest advances in satellite technology and spacecraft systems design.
Learn more about the Marjorie Rhodes Townsend papers here:
http://ead.lib.virginia.edu/vivaxtf/view?docId=vt/viblbv00183.xml;query=;
L. Jane Hastings: Architect, Business Owner
As an eighth-grade student, L. Jane Hastings was told that women could not be architects. When she secured a coveted spot in the University of Washingtons architecture program, Hastings recalls being asked to give up her place to make room for returning veterans. Hastings received her Bachelor of Architecture degree with honors in 1952, having worked full-time throughout most of her program. In 1953, she became the eighth licensed woman architect in the State of Washington. Hastings founded her own practice in 1959 and went on to form the Hastings Group, a prestigious firm that completed over 500 residential, commercial, and university projects across the greater Seattle area. In addition to practicing and teaching architectural design, Hastings was active in several professional organizations. In 1992, Hastings was appointed the first woman chancellor in the American Institute of Architects College of Fellows.
Learn more about the L. Jane Hastings Architectural Papers here:
http://ead.lib.virginia.edu/vivaxtf/view?docId=vt/viblbv00138.xml
Dr. Laura Jane Harper: Academic Dean, Advocate

Dr. Laura Jane Harper was the first woman to serve as an academic dean at VPI. She lead the College of Home Economics from 1960-1980, chartering a new program that emerged from the consolidation of the Home Economics programs at VPI and Radford University. Dr. Harper was lauded for mentoring other women and supporting them in leadership positions throughout the university. In her 1999 Masters thesis A Fighter To The End: The Remarkable Life and Career Of Laura Jane Harper, Saranette Miles recounted Dr. Harpers decision to turn down a marriage proposal for the sake of her career (p. 55) and how she frequently challenged VPI President T. Marshall Hahn to uphold his commitments to create meaningful opportunities for women at the university (p. 70-75) .
Read more about Harpers career and her contributions to the Peacock-Harpery Culinary Collection:
https://whatscookinvt.wordpress.com/2015/03/06/whm-laura-harper/
Linda Adams Hoyle: Statistician, Trailblazer

Linda Adams Hoyle (class of 68) was the first black woman to graduate from Virginia Tech. As a statistics major, Hoyle was frequently the only woman in her classes and one of few black students. Her experiences on campus – friendships, dorms assignments, political activism, and safety concerns – were shaped by the intersection of race and gender. After graduation, Hoyle went on to work as a statistician for the Census Bureau in Washington, D.C.In her oral history interview for the Black Women At Virginia Tech History Project, Hoyle discussed the challenges of raising a family while pursuing a career:
.. So when you have this full time career–my job at that time was extremely demanding. It was difficult because I had to attend to my children as well as do the job.My husband, the way he worked, it was difficult. He could not just stop in the middle of a job say to pick up a sick child. His work did not permit him that flexibility. Those were things I had to do.
Read Linda Adams Hoyles Oral History Interview:
http://spec.lib.vt.edu/archives/blackwomen/adams.htm
Learn more about the experiences of Virginia Tech’s first black students:
http://www.vtmag.vt.edu/sum14/trailblazers-black-alumni-60s-70s.html